www.space.com
Mars sample return mission adds 2 helicopters, scraps 'fetch' rover
The redesigned NASA-European campaign will task the Perseverance rover with delivering Red Planet samples to a rocket, with the drones as backup retrieval options.
Science & Tech
The campaign to bring pristine Martian samples to Earth will now include two mini helicopters.
NASA officials involved with the Mars sample return (MSR) effort announced today (July 27) that they plan to redesign the mission, abandoning a previous concept that called for a European Space Agency (ESA) "fetch rover" that would touch down on its own lander.
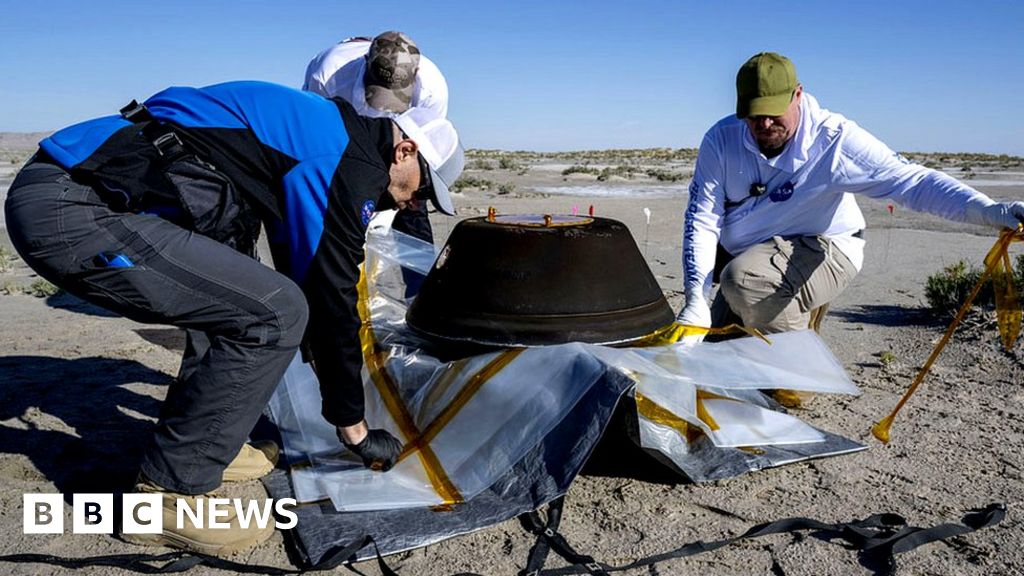
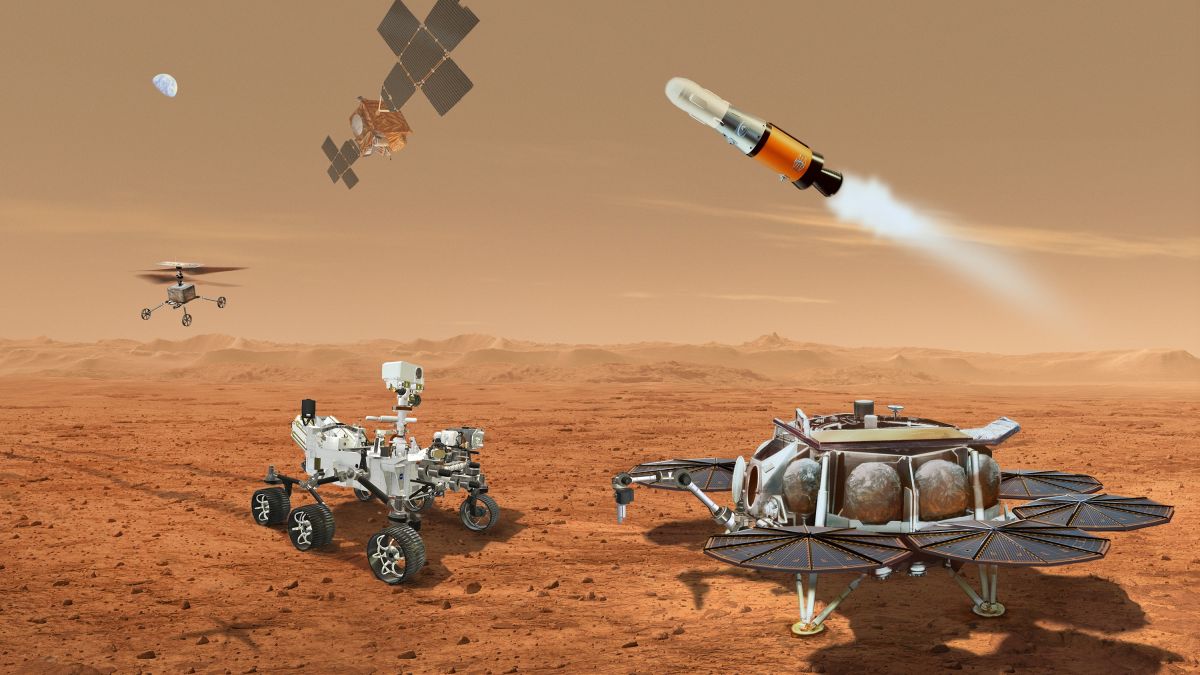
NASA's Perseverance rover, expected to still be active when a NASA MSR lander touches down in 2031, will now be tasked with bringing the samples it is collecting and caching to a Mars ascent vehicle. Failing that, however, two helicopters much like Ingenuity, which landed with Perseverance last year, will be backup options to pick up the caches themselves.
The helicopters will be similar to Ingenuity in terms of size and mass, but with two key differences, NASA MSR program manager Richard Cook told reporters during a briefing today.
"There will be landing legs that include, at the bottom of them, mobility wheels," Cook explained, saying this new capability will allow the helicopters to "traverse across the surface." A mini robotic-arm on each of the craft will allow the drones to pick up the sample tubes Perseverance leaves behind, if need be.
If the helicopters are needed for such work, they will land near a sample tube, roll over to pick it up, then fly to a spot near the Mars ascent vehicle. After touchdown, the helicopters will roll closer to the vehicle and drop the sample within reach of a newly announced ESA-built transfer arm.
The redesign decision means that no ESA rover will touch down on Mars in the near future. But the new concept also may allow NASA and ESA to accomplish the ambitious sample return effort with less cost and complication, according to the coalition.
"The engineer in me was fascinated by the sample rover, because it's designed to travel much faster than previous Mars rovers, probably about four or five times as quickly over the surface," David Parker, director of ESA's human and robotic exploration, told reporters today.
Adding the rover, however, would have entailed "a second launch, second lander and so forth," which meant that removing the hardware from the manifest "makes a great deal of programmatic sense," he said.
ESA is still building a rover tasked with landing on Mars — a life-hunting robot named Rosalind Franklin. That rover was supposed to launch this year on a Russian rocket, but that plan fell through after Russia invaded Ukraine. Rosalind Franklin is now expected to lift off no earlier than 2028.
"The engineering team has been working at great speed to find an alternative approach for delivering Rosalind Franklin rover to Mars," Parker said of the situation, saying different options are under discussion. A special European council meeting in Paris in November will allow member states to decide the best path forward, he added.