interestingengineering.com
NASA's Parker Solar Probe Sets Two Records on Its Latest Solar Slingshot
The event marked both the closest satellite to survive such a near pass of the Sun and the fastest-ever artificial object.
Science & Tech
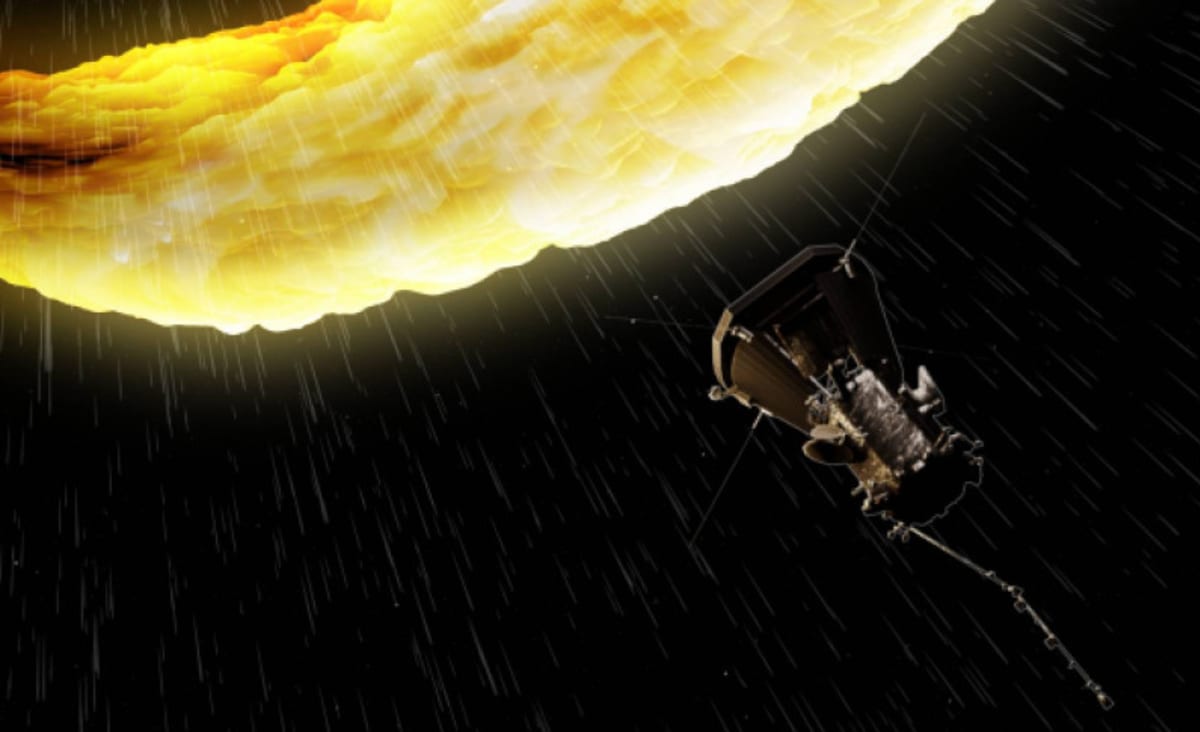
NASA's Parker Solar Probe has survived yet another close encounter with the Sun (its 10th) breaking two more world records in the process according to a NASA press release. It all happened on November 21, 2021 at 4:25 am EST (08:25 GMT) when the explorer came within 5.3 million miles (8.5 million km) of the Sun's surface at a speed of 363,660 mph (586,864 km/h).
These specifications made it both the closest satellite to survive such a near pass of the Sun and the fastest-ever artificial object. NASA and mission operators at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, reported that the craft is in good condition and operating optimally and will begin sending data on December 24 and end on January 9, 2022.
The record-breaking milestone marked the midway point in the Parker Solar Probe's 10th solar encounter, which began Nov. 16 and continues through Nov. 26.
In total, Parker Solar Probe plans to complete 24 increasingly closer orbits to the Sun using the gravitational pull of Venus. The spacecraft is set to come within 4.3 million miles (6.9 million km) of the surface of the Sun and reach speeds of over 430,000 mph (690,000 km/h).
Of course, with crafts heading so close to a star, there is the issue of radiation. Parker Solar Probe is however heavily shielded against heat and radiation, but it is still susceptible to damage.
In its trips to the sun, it accumulates dangerous electrical charges from solar radiation. To counter this problem, NASA scientists have made its orbit highly elliptical to allow it to recover between such dangerously close encounters.
Parker Solar Probe is meant to communicate back to Earth data largely covering the properties and structure of the solar wind as well as the dust environment near the Sun.