www.goodnewsnetwork.org
Tick-Borne Infection Immune to Most Antibiotics May Be Blocked Using Special ‘Nanobodies’
In cells and mice, tiny molecules stop tick-spread bacteria from hijacking cells, according to new research from Ohio State.
Health
Tiny molecules called nanobodies, which can be designed to mimic antibody structures and functions, may be the key to blocking a tick-borne bacterial infection that remains out of reach of almost all antibiotics, new research suggests.
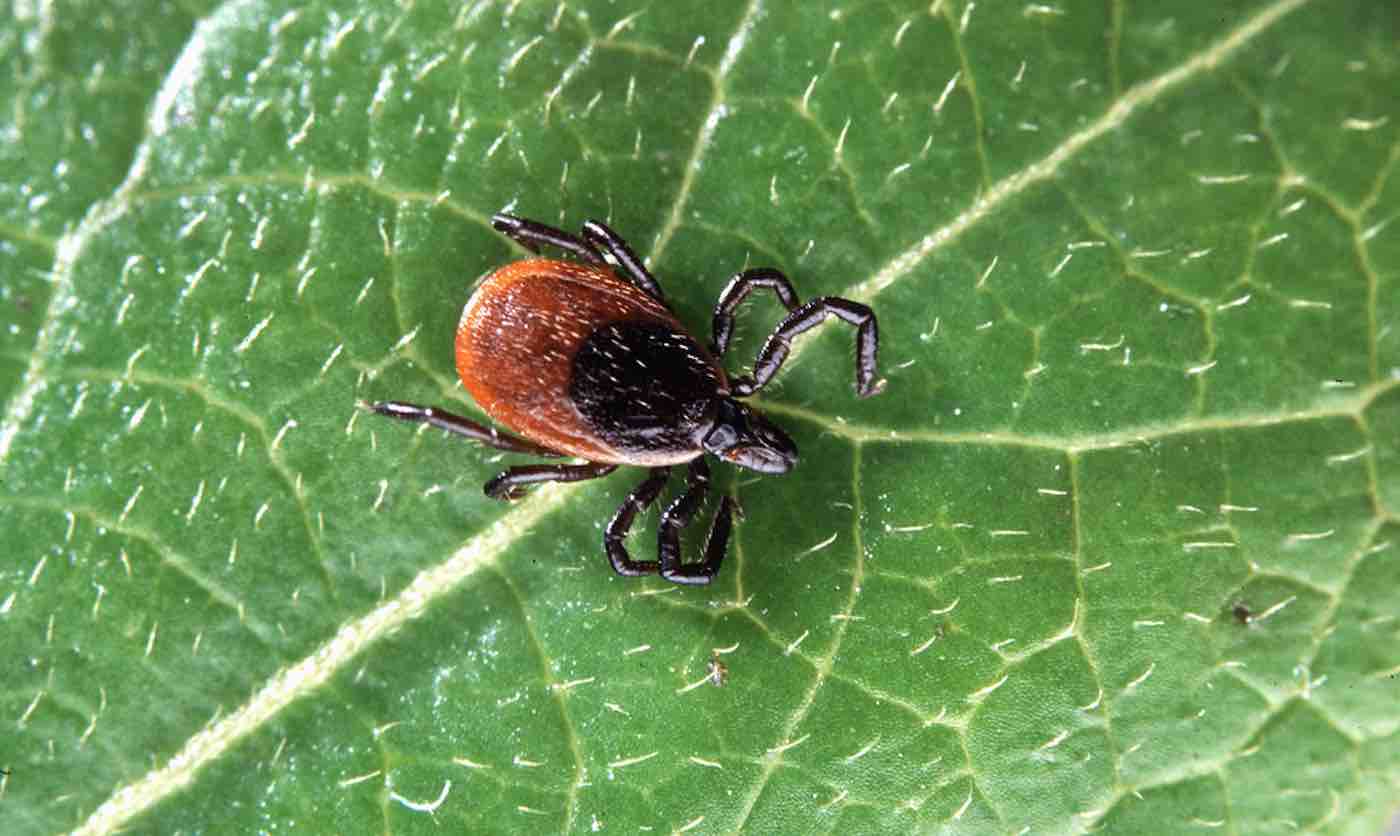
The infection is called human monocytic ehrlichiosis (HME), and is one of the most prevalent and potentially life-threatening tick-borne diseases in the United States. The disease initially causes flu-like symptoms common to many illnesses, and in rare cases can be fatal if left untreated.
Most antibiotics can’t build up in high enough concentrations to kill the infection-causing bacteria, Ehrlichia chaffeensis, because the microbes live in and multiply inside human immune cells. Commonly known bacterial pathogens like Streptococcus and E. coli do their infectious damage outside of hosts’ cells.
Ohio State University researchers created nanobodies intended to target a protein that makes E. chaffeensis bacteria particularly infectious.
A series of experiments in cell cultures and mice showed that one specific nanobody they created in the lab could inhibit infection by blocking three ways the protein enables the bacteria to hijack immune cells.
“If multiple mechanisms are blocked, that’s better than just stopping one function, and it gives us more confidence that these nanobodies will really work,” said study lead author Yasuko Rikihisa, professor of veterinary biosciences at Ohio State.
The study provided support for the feasibility of nanobody-based ehrlichiosis treatment, but much more research is needed before a treatment would be available for humans. There is a certain urgency to coming up with an alternative to the antibiotic doxycycline, the only treatment available. The broad-spectrum antibiotic is unsafe for pregnant women and children, and it can cause severe side effects.
“With only a single antibiotic available as a treatment for this infection, if antibiotic resistance were to develop in these bacteria, there is no treatment left. It’s very scary,” Rikihisa said.